Vertical Summary - Permanent Device Identities
Definitions
Acronym | Definion |
|---|---|
BC | Birth Certificate |
BYORoT | Bring your own root of trust. A program developed between Keyfactor an device manufacturer (e.g., Infineon/Microchip/etc.) that allows OEMs to provision secure elements off of the OEM manufacturer’s PKI. This limits the ability of contract manufacturers to counterfeit devices. |
IDC | Initial Device Certificate - this is permanent on the device in this use case |
OEM | Original Equipment Manufacturer |
Use case
Device manufacturer wants to inject certificates into products for device-specific permanent certificates (IDC).
Option #1 - using BYORoT only
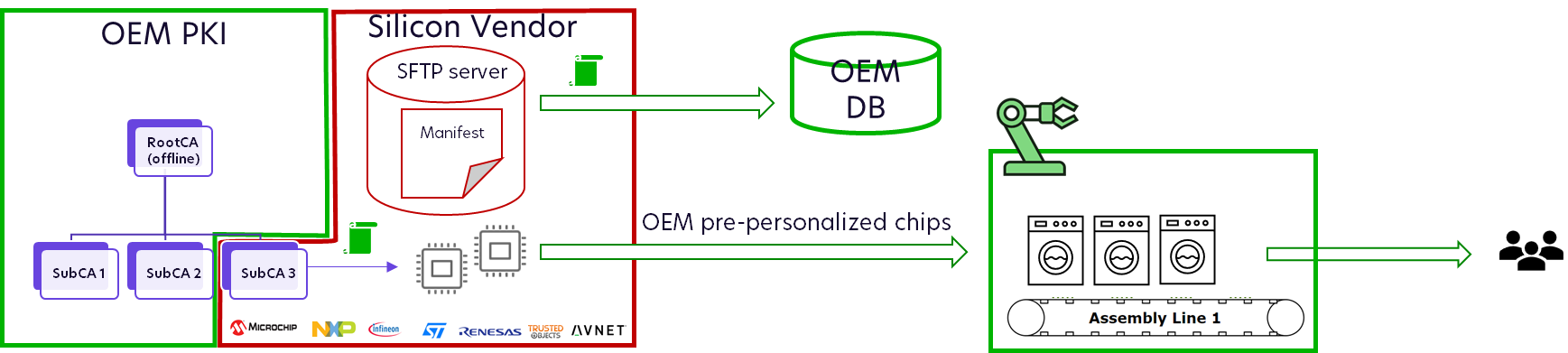
OEM sets-up his PKI for Initial Device Certificates and signs issuing CAs for Silicon Vendor or distributor factory
OEM orders pre-programmed secure elements or MCUs from Silicon Vendor or distributor
Silicon is pre-provisioned securely with unique device manufacturer permanent Initial Device Certificates from the device manufacturer’s PKI
Silicon Vendor ships reels of chips to device manufacture’s factory (or a contract manufacturer) and sends corresponding production manifest to manufacturer
Chips are mounted on device printed circuit board
Device is ready to boot with a unique Manufacturer’s Initial Device Certificate
Benefits
Simplest configuration
Very cost effective
No PKI or PKI access required at contract manufacturer
Can swap contract manufacturers whenever required
Limitations
Must have a single issuing CA for all devices
If a device’s cert ever expired, the use case is undefined, even with reenrollment
Option #2 - using BYORoT and EJBCA with EST
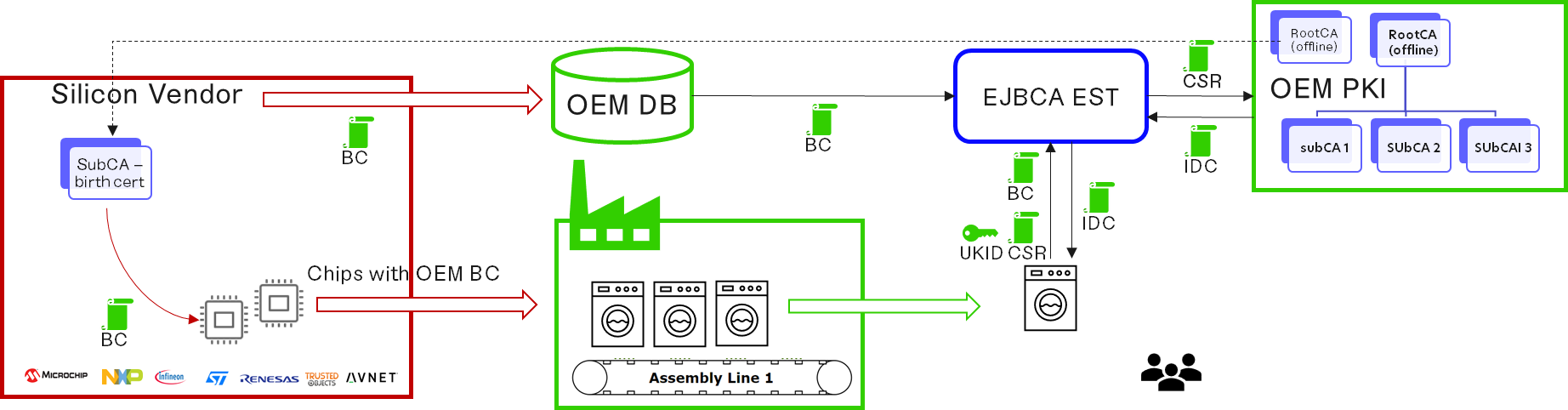
What is needed:
A PKI set-up and ready to issue the IDC with an RA reachable over the Internet
Devices with a unique Birth Certificate which can be traced back to a Root CA owned by the Device Manufacturer
An inventory of these Birth Certificates, not only purchased by the Device Manufacturer, but tagged as mounted into the devices manufactured
The enrollment of the device can be directly performed by EJBCA using EST Client Mode - Vendor Certificate Authentication: https://doc.primekey.com/ejbca/ejbca-operations/ejbca-ca-concept-guide/protocols/est/est-client-mode-configuration .
Secure the connection to the RA
Set up a reverse proxy in front of the RA for mTLS.
Configure the proxy to only trust the Root CA that signed the SubCA-Birthcert given to the Silicon Vendor
The BC issuing CA is specific to the Device Manufacturer (Microchip Trust&Flex for instance), not “generic”. Then the RA proxy can filter connection requests to OEM devices only. We recommend that the OEM uses our BYORoT program to tie the BC issuing CA to his own PKI.
At Silicon Manufacturer
Inject a BC into the OEM chip; this BC comes from an Issuing CA (Policy CA) specifically provisioned for the OEM.
At manufacturing
The Root Certificate of the proxy certificate chain must be provisioned in the device trust store
Required to trust the proxy certificate
A UKID is computed by the device: hash of the BC public key
This UKID is then made the username of an End Entity which must be created in EJBCA RA for future IDC issuance
This UKID must be stored in the device memory for later use.
IDC Enrollment
The device needs to contact the RA proxy attached to the issuing CA it is requesting the IDC from.
mTLS must be established
The device sends a request to the /cacerts EST endpoint to download the Root CA Certificate defined in the EST Alias.
The device generates a new key pair
The device creates a PKCS#10/CSR for the IDC, using the UKID in a DN field
The device sends the PKCS#10/CSR to the simpleenroll EST endpoint
Upon matching the UKID to an end entity in EJBCA, the IDC is issued and sent back to the device
The IDC can be exported from EJBCA and provisioned at will
If the Silicon Vendor offers the option, the BC can be revoked
In the field - reenrollment
Secure the connection to an externally facing RA
Set up a proxy using the Root CA for the IDC
In case a device would need to renew its IDC, it would use its about-to-expire IDC for the mTLS link to the RA proxy.
In this case, another proxy would need to be configured to trust the about-to-expire IDC issuing certificate which then could be used for the mTLS connection.
Limitations
BC, EST endpoint and IDC issuing CA are product-specific
Can only have one EST endpoint for all devices
Must have a single issuing CA for all devices
Can only vet one UKID or shared secret
The IDC must never expire
If a device’s IDC cert ever expired, the use case is undefined, even with reenrollment
Option #3 - Using Silicon vendor’s PKI with EJBCA in EST mode
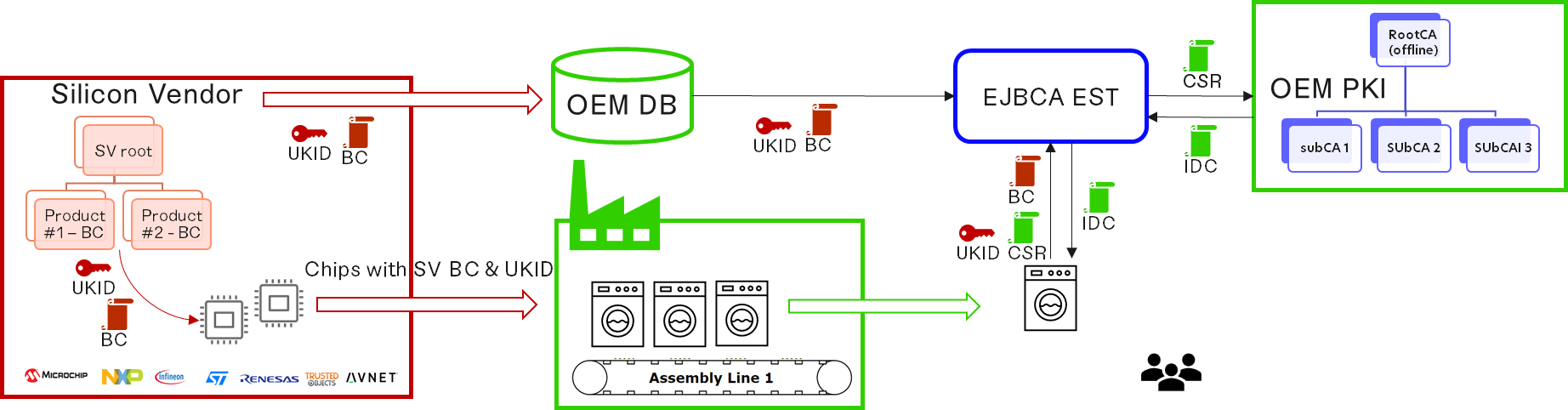
What is needed:
A PKI set-up and ready to issue the IDC with an RA reachable over the Internet
Devices with a unique Birth Certificate and secret UKID from the silicon vendor
An inventory of these Birth Certificates and UKID, not only purchased by the OEM, but tagged as mounted into the devices manufactured
The enrollment of the device can be directly performed by EJBCA using EST Client Mode - Vendor Certificate Authentication: https://doc.primekey.com/ejbca/ejbca-operations/ejbca-ca-concept-guide/protocols/est/est-client-mode-configuration .
Secure the connection to the RA
Set up a reverse proxy in front of the RA for mTLS.
Configure the proxy to only trust the Root CA that signed the SubCA-Birthcert given to the Silicon Vendor
The BC issuing CA is “generic” (Microchip Trust&Go for instance). The RA proxy will accept a connection from any device with the same issuing CA, beyond OEM devices. This option increases the attack surface of the PKI RA.
At Silicon Manufacturer
Inject a BC into the OEM chip; the BC comes from an Issuing CA (Policy CA) owned and managed by the silicon vendor and shared with all his customers.
Inject a UKID (shared secret) into the OEM chip.
At manufacturing
The Root Certificate of the proxy certificate chain must be provisioned in the device trust store
Required to trust the proxy certificate
The UKID is made the username of an End Entity which must be created in EJBCA RA for future IDC issuance
IDC Enrollment
The device needs to contact the RA proxy attached to the issuing CA it is requesting the IDC from.
mTLS must be established
The device sends a request to the cacerts EST endpoint to download the Root IDC Certificate
The device generates a new key pair
The device assembles a CSR for the IDC, using the UKID in a DN field
The device sends the CSR to the simpleenroll EST endpoint
Upon matching the UKID to an end entity in EJBCA, the IDC is issued and sent back to the device
The IDC can be exported from EJBCA and provisioned at will
If the Silicon Vendor offers the option, the BC can be revoked
In the field - reenrollment
Secure the connection to an externally facing RA
Set up a proxy using the Root CA for the IDC
In case a device would need to renew its IDC, it would use its about-to-expire IDC for the mTLS link to the RA proxy.
In this case, another proxy would need to be configured to trust the about-to-expire IDC issuing certificate which then could be used for the mTLS connection.
Limitations
UKID required in the personalization profile provided by the silicon vendor
EST endpoint and IDC issuing CA are product-specific
Can only have one EST endpoint for all devices
Must have a single issuing CA for all devices
Can only vet one UKID or shared secret
The IDC must never expire
If a device’s cert ever expired, the use case is undefined, even with reenrollment
